Imagine you are working on a sales analysis project for a retail store. You’ve been given access to their sales database, which contains tables for customers, products, and sales transactions. Your goal is to gain insights into customer preferences, product performance, and overall sales trends.
In this scenario, you might encounter the following common SQL errors while performing data analysis:
Error: Incorrect syntax near ‘keyword’
![]()
Common causes:
- Misspelled keywords or table names
- Missing or misplaced SQL keywords like SELECT, FROM, or WHERE
Solutions:
- Double-check the spelling of all keywords and table names
- Make sure all required keywords are in place
Corrected example:
![]()
Error: Ambiguous column name ‘column_name’

Common causes:
- Columns with the same name in different tables without proper aliasing
Solutions:
- Use table aliases and/or column aliases to avoid ambiguity
Corrected example:

Error: Invalid column name ‘column_name’
![]()
Common causes:
- Typo in the column name
- Using a non-existent column name
Solutions:
- Double-check the spelling of the column names
- Verify the correct column name from the table schema
Corrected example:
![]()
Error: Conversion failed when converting the varchar value ‘value’ to data type int
![]()
Common causes:
- Comparing or combining different data types without proper conversion
Solutions:
- Use the appropriate data type for the value being compared or combined
- Use explicit conversion functions like CAST() or CONVERT() if necessary
Corrected example:
![]()
Error: The multi-part identifier “table_name.column_name” could not be bound
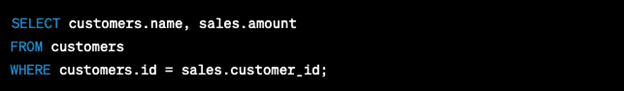
Common causes:
- Missing a required table in the FROM clause or a JOIN statement
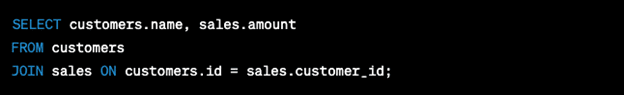
Solutions:
- Ensure all relevant tables are included in the FROM clause or are properly joined
Corrected example:
By addressing these common SQL errors, you can effectively troubleshoot your data analysis queries and continue to derive valuable insights from the retail store’s sales data.