
Have you ever wished you could harness the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to boost your productivity or pursue your personal interests, but felt daunted by the technical complexity of AI tools? You’re not alone. Many non-technical users are intrigued by the potential of generative AI tools, yet feel unsure about how to effectively use them. This is where prompt engineering comes into play.
Prompt engineering is the process of carefully crafting input prompts to guide generative AI tools in producing the desired output. It’s akin to giving precise instructions to a skilled assistant. In fact, you’ve likely engaged in a similar activity when using a search engine. When you type a query into Google, you’re essentially crafting a prompt to guide the search engine in providing the most relevant results. The more specific and clear your query, the better the results.
By mastering the art of prompt engineering, you can unlock the full potential of generative AI tools, turning them into powerful allies that can help you achieve your goals. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of prompt engineering, exploring its key concepts, benefits, and practical applications. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence you need to leverage generative AI tools to your advantage, whether it’s for boosting your productivity at work or exploring your personal interests.
The Art and Science of Prompt Engineering in Generative AI
What is a prompt?
A prompt, in the context of generative AI tools, is a message or set of instructions that you provide to the AI system to guide its output. When you ask a generative AI tool a question or give it a command, you are essentially creating a prompt. The prompt acts as the starting point for the AI to generate a response or complete a task.
What is the purpose of a prompt?
The primary purpose of a prompt is to direct the AI’s response in a way that meets the user’s needs. A well-crafted prompt helps the AI understand what is being asked and generates a more accurate and relevant output. The purpose of a prompt may vary slightly depending on the specific generative AI tool you are using. For example, when using a language generation tool, the prompt might be a sentence or question that you want the AI to continue or answer. In contrast, when using an image generation tool, the prompt might be a description of the image you want the AI to create. Example of a prompt for a text-based output:

Prompts initiate and guide the generation process.
In addition to guiding the AI’s output, prompts can also be used to engage in a “conversation” with the AI tool. This conversational approach allows users to refine and clarify their requests based on the AI’s responses, ultimately leading to more meaningful and usable output. By treating the interaction with the AI as a dynamic conversation, users can iteratively refine their prompts and the AI’s responses, creating a feedback loop that results in increasingly accurate and helpful outputs.
This conversational aspect of prompt engineering is particularly valuable when dealing with complex or nuanced tasks. It enables users to build upon the AI’s responses, ask follow-up questions, and provide additional context or clarification to guide the AI towards the desired outcome. In essence, the prompt becomes a tool for collaboration between the user and the AI, with the goal of achieving a shared understanding and a successful outcome.
Prompt engineering plays a crucial role in making generative AI accessible and useful to a wide range of users and applications.
Effective prompt engineering ensures that generative AI isn’t confined to the domain of tech-savvy experts. Even individuals without deep AI knowledge can leverage it for tasks like content creation, data analysis, and more, given the right prompts. From education and entertainment to business strategy and scientific research, prompt engineering adapts generative AI outputs to resonate with the unique demands and nuances of each sector.
Decoding Prompt Engineering in Generative AI
Prompt engineering is a dynamic and iterative process that involves continuous learning and improvement.
Engineering a prompt involves carefully crafting your input to achieve the desired output from the AI. Here are some steps to consider:
- Start by clearly defining the goal of your prompt. What do you want the AI to generate or do? Having a clear objective will guide the entire prompt engineering process.
- Make your prompt as specific and detailed as possible. The more information you provide, the better the AI can understand and fulfill your request. Consider including relevant context or examples to help clarify your request.
- Test and refine your prompt. Once you have crafted your prompt, input it into the AI tool and analyze the output. If the AI’s output is not what you expected, consider tweaking your prompt and trying again.
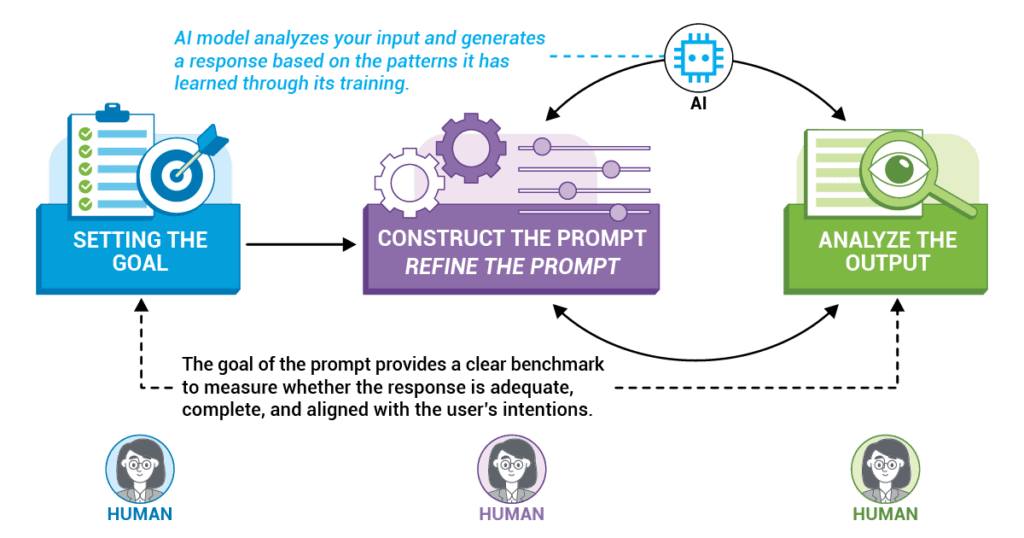
The process of engineering a prompt is often iterative and requires a willingness to experiment and refine your input. It is a common misconception that AI tools should understand and respond accurately to any input, regardless of how it is phrased. However, the reality is that the quality of the output is heavily dependent on the quality of the input. By taking the time to carefully craft and refine your prompts, you can significantly improve the accuracy and relevance of the AI’s output.
Moreover, the iterative nature of prompt engineering allows you to build a deeper understanding of how the AI tool interprets and responds to different inputs. This knowledge can be invaluable in achieving the desired outcome, especially for complex or nuanced tasks. In essence, prompt engineering is not just about crafting the perfect input; it is also about learning and adapting to the AI tool’s capabilities and limitations.
Prompt engineering helps in managing the trade-off between the AI’s creativity and control.
One of the grand challenges in AI is managing its boundless creativity while ensuring it remains within desired bounds. A broad, open-ended prompt might let the AI’s creativity run wild, while a tight, specific one could reign it in. Through prompt engineering, users can glide seamlessly along this spectrum, depending on their needs.
Prompt engineering contributes to the transparency and trust in generative AI models.
In an age where trust in technology is paramount, prompt engineering stands as a sentinel of transparency and predictability. By understanding how the AI reacts to different prompts, users can better anticipate its behavior, fostering trust. Observing AI responses to varied prompts provides invaluable insights into its decision-making mechanics, demystifying the often opaque processes of advanced AI models.
Navigating the Hurdles: Challenges in Prompt Engineering
Lack of universally accepted definitions or standards
As we delve deeper into the realm of prompt engineering, it’s essential to recognize that this field, much like the broader AI landscape, is in a constant state of flux. AI isn’t a stagnant technology; it evolves at a dizzying pace. As new breakthroughs emerge and challenges surface, the methodologies for crafting effective prompts must keep pace, adapting and innovating.
Crafting a prompt is a complex process
Behind every successful interaction with generative AI is a well-phrased prompt, but arriving at this golden query is no straightforward task. To engineer an effective prompt, one must have a foot in two worlds: a profound understanding of the AI model’s intricacies and an acute awareness of the problem or task being addressed. It’s like trying to write a novel when you’re deeply aware of the nuances of the language while also staying true to the plot’s intricacies.
The capabilities and limitations of the AI model
Even the most meticulously crafted prompt can’t transcend the boundaries set by the AI model it’s interacting with. Generative AI models have a vast but finite understanding. No matter how adeptly a prompt is designed, if the information or pattern isn’t within the model’s grasp, the desired output remains elusive. AI models, in their training, can inadvertently adopt biases or misconceptions present in the training data. Consequently, even with a perfect prompt, the outputs might reflect these embedded flaws. Imagine asking a wise sage a question, but the answer, while profound, carries the biases of the books they’ve read.
Case Study: Alex Learns to Unlock the Power of Generative AI
Alex is passionate about environmental conservation. He has recently heard about generative AI tools and is curious to learn how they can help him spread awareness about recycling among his peers.
Alex decides to explore a generative AI tool to create content for his environmental club’s social media page. His initial approach is to simply input “Create a post about recycling” into the AI tool. The output is a generic message that lacks the impact he was hoping for. This is when Alex realizes that he needs to learn more about how to effectively communicate with the AI tool to get the desired results.
Alex starts researching about prompt engineering and learns that the quality of the output is heavily dependent on the quality of the input. He understands that a prompt is not just a command; it is a way to guide the AI tool’s response in a specific direction. The purpose of a prompt is to clearly communicate the user’s intent and provide enough context for the AI tool to generate relevant and accurate output.
With this newfound knowledge, Alex decides to engineer his prompt more carefully. He inputs, “Create a compelling social media post that highlights the importance of recycling, includes a shocking statistic about landfill waste, and ends with a call-to-action for people to start recycling.” This time, the AI tool generates a post that perfectly aligns with Alex’s vision.
Through this process, Alex learns the importance of being specific and clear when crafting prompts. He also realizes that prompt engineering is an iterative process that may require testing and refining the input to achieve the desired outcome. Most importantly, Alex discovers that by mastering the art of prompt engineering, he can unlock the full potential of generative AI tools and use them as a powerful ally in his mission to promote environmental conservation.