Table of Contents
Toggle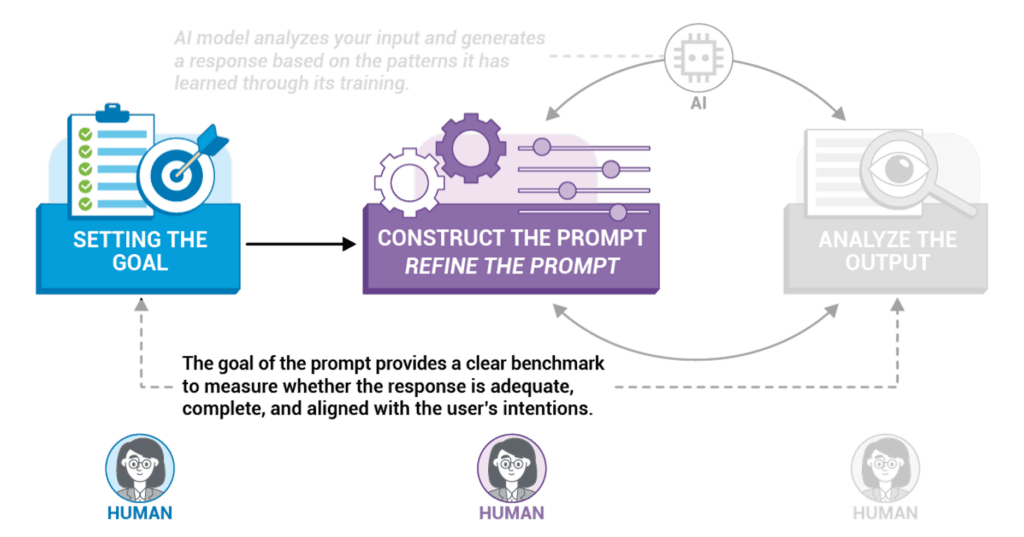
Prompt engineering is a crucial skill for users looking to fully leverage the capabilities of generative AI tools. By understanding and mastering the initial steps of setting clear, specific goals and meticulously constructing prompts, users can begin to effectively communicate their needs to AI tools, resulting in outputs that are not only more accurate and relevant but also tailored to enhance productivity and support personal interests.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of these foundational steps of the prompt engineering process, providing practical tips and illustrative examples to empower you to harness the full potential of generative AI tools.
Setting the Goal: The Foundation of Prompt Engineering
Setting a clear and specific goal is the first and most crucial step in the prompt engineering process. The goal acts as the foundation that guides the entire process, from constructing the prompt to analyzing the output.
- Identifying the problem
Start by clearly defining the problem or challenge you want to address. Ask yourself what issue or question you want the AI tool to help you solve. Identifying the problem sets the direction for the prompt engineering process. A clear understanding of the problem ensures that the AI tool is focused on providing a relevant and useful solution.
Some problems are simple to identify, while others are more challenging. One technique to consider is the use of “5 Whys.”
In the context of the problem formulation process for prompt engineering, the “Five Whys” technique can be used as follows:
-
Start with the initial Problem statement:
- Begin by stating the problem you are facing. For example, “The AI tool is not generating the desired output.”
-
Ask the first Why:
- Ask why the problem is occurring. For example, “Why is the AI tool not generating the desired output?”
- Answer: “The output is not specific enough.”
-
Ask the second Why:
- Ask why the first answer is occurring. For example, “Why is the output not specific enough?”
- Answer: “The prompt is too vague.”
-
Continue the process:
- Continue asking “why” and providing answers until you reach the root cause of the problem. This might involve asking “why” more than or less than five times, depending on the complexity of the issue.
-
Identify the root cause:
- Once you reach an answer that reveals the fundamental cause of the problem, you have identified the root cause. For example, “The prompt is too vague because I am not sure what specific information to include.”
- Determining the desired outcome
Once the problem is identified, consider what a successful outcome would look like. Define the specific results or answers you hope to achieve with the help of the AI tool. Determining the desired outcome helps to set clear expectations for the AI tool’s output. This step ensures that you have a benchmark against which to assess the AI tool’s performance.
- Defining the constraints
Consider any limitations or boundaries within which the AI must operate. These could include specific requirements or restrictions that apply to the task. For example, if you’re using an AI tool to generate a short story, your constraints could be “The story should be no more than 500 words long and should be appropriate for a high school audience.” Defining the constraints ensures that the AI tool’s output meets your specific requirements and adheres to any necessary limitations. This step helps to set realistic expectations and ensures that the AI tool’s capabilities are aligned with your needs.
- Formulating a clear objective for the AI
Based on the identified problem, desired outcome, and defined constraints, formulate a clear and concise objective for the AI tool. This should be a specific statement that communicates what you want the AI tool to achieve. A clear objective provides a focused direction for the AI tool, ensuring that it is aligned with your needs and expectations. This step is crucial for guiding the AI tool towards providing a relevant and useful solution.
Constructing the Prompt: Crafting Your Request
Once you have a clear goal in mind, the next step is to construct the prompt. This involves carefully crafting the input to guide the AI tool towards generating the desired output.
Here are the key components involved in constructing prompts:
- Choose a prompt pattern that aligns with your objective
The first step in constructing a prompt is to select a structure that aligns with your objective. Prompt patterns are essential to effective prompt engineering because they provide a structured approach to guide the AI in generating the desired output. The pattern serves as a blueprint that shapes the AI’s response, ensuring that it aligns with the user’s objectives. When considering different prompt structures, think about the nature of your objective and how the structure might influence the AI’s output. For example, if your objective is to generate a creative story, a narrative structure might be most appropriate.
Here are some reasons why prompt patterns are crucial:
Aligns with objectives: A prompt pattern that is well-aligned with the user’s objectives helps to guide the AI in generating output that meets the user’s needs. It ensures that the AI understands the task and produces relevant results.
Improves consistency: Using a prompt pattern can improve the consistency of the AI’s output. It provides a structured approach that can be replicated across different tasks, ensuring that the AI responds in a consistent manner.
Facilitates clear communication: A prompt pattern helps to facilitate clear communication between the user and the AI. It provides a structured format that makes it easier for the user to communicate their needs and expectations to the AI.
Enhances creativity: In some cases, a prompt pattern can enhance the creativity of the AI’s output. By providing a structured approach, the AI can focus on generating creative content within the defined parameters, leading to more innovative results.
Supports iterative refinement: Prompt patterns support the iterative refinement of prompts. If the initial output is not satisfactory, the user can adjust the pattern to improve the AI’s response, leading to more accurate and relevant results.
Increases efficiency: A prompt pattern can increase the efficiency of the prompt engineering process. It provides a clear and structured approach that reduces the time and effort required to generate effective prompts.
In summary, prompt patterns are a crucial component of effective prompt engineering. They provide a structured approach that aligns with the user’s objectives, improves consistency, facilitates clear communication, enhances creativity, supports iterative refinement, and increases efficiency.
- Assign author and audience roles
Define who is “speaking” in the prompt and who the intended audience is. This helps to establish the context and tone of the prompt. For example, if you are generating content for a business presentation, the author might be a business professional, and the audience would be colleagues or clients. - Write instructions
Include specific directions that guide the AI in generating the desired output. Clearly state what you want the AI to do. Instructions should be detailed and explicit to ensure the AI understands the task and can generate the output accordingly. - Add examples
Provide examples that serve as models for what the desired output should look like. This helps to clarify the expectations and guide the AI towards producing a similar output. For example, if you are generating a poem, you might include an example of a poem that has a similar style or theme to what you want. - Fill in context or missing information
Consider what information the AI might not have access to and include it in the prompt. This ensures that the AI has all the necessary information to generate the desired output. For example, if the AI model was not trained on recent data, you might need to provide up-to-date information to ensure the output is relevant and accurate. - Ask for feedback
Encourage the AI to engage in a dialogue to refine the output. This could involve asking follow-up questions, suggesting alternatives, or proposing improvements. For example, you could instruct the AI to “Ask for clarification if any part of the task is unclear, or suggest alternative plot points if necessary.”
By carefully constructing the prompt and considering each of these components, you increase the likelihood that the AI tool will generate an output that meets your needs and expectations.